Fungal
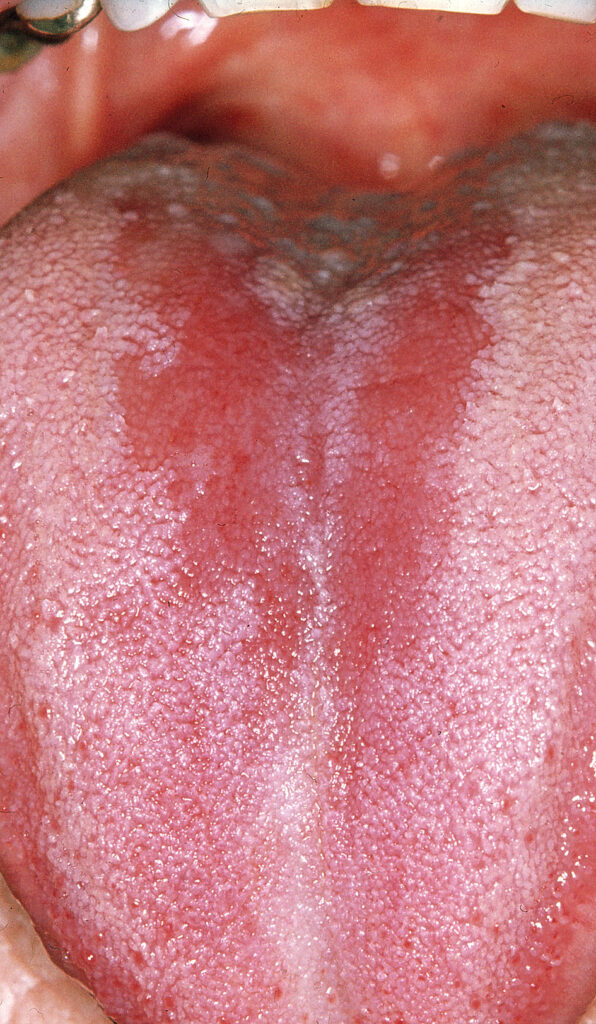
Fungal diseases can manifest on gums and soft tissues. It can be seen in children and under dentures. Fungus is a natural part of our oral flora, but if growth conditions are improved, it can grow uncontrolled. It is not contagious by physical contact.
Fungus in the oral cavity can look very different. It can show up as whitish scraped off coatings or red changes. The whites give no symptoms, but the reds can cause irritation and burning when consuming especially strong foods. Untreated, it can become chronic and develop into whitish areas that cannot be scraped off and are asymptomatic.
The most common reason for a fungal infection is after the use of antibiotics. Antibiotics kill the bacteria in the mouth, but not the fungus, and the fungus is allowed to spread. Causes can also be: reduced immune system, vitamin deficiency, anemia, or general disease such as. diabetes, smoking, decreased saliva, other oral mucosal disease, e.g. oral lichen planus, use of dentures, poor oral and / or prosthetic hygiene, large intake of sweets and sodas and local effects of medication.
Fungus in the oral cavity can be reduced by:
- Having a good oral hygiene
- Avoid smoking
- If you suffer from lack of saliva, then stimulate production (chewing gum, tablets or the like).
- Rinse mouth with water and saliva after using inhalator
Treatment is done with fungicide in the form of tablets (usually 2-4 weeks), oral gel or oral solution (usually 4-6 weeks). Always remember to state your medication consumption. The antifungals can inhibit the effect of medication.
Virus
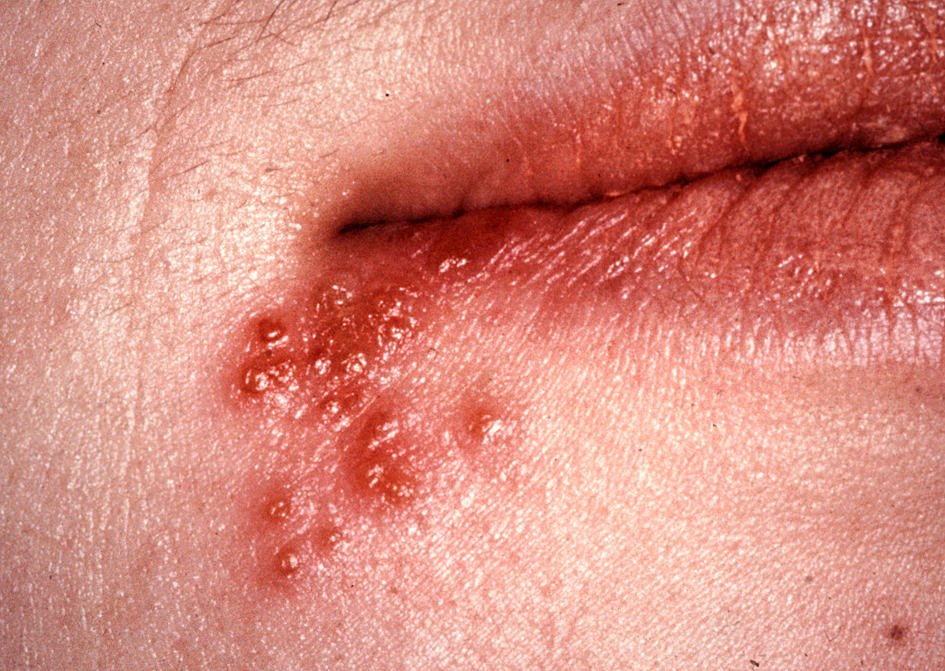
If you have a recurrent cold sore, it is cost by herpes virus. The wound may occur on the lips and / or in the mouth. The disorder is common. Ca. 80% are carriers of the herpes virus.
The first time you get infected with the herpes virus, there will probably be no symptoms. However, small children will often get symptoms. These manifest as blisters and sores on the lips / mouth, malaise, fever, difficulty eating.
Upon reactivation of the virus, the symptoms will appear as the tingling in the lip followed by small blisters that rupture and form a wound crust that heals. It can hurt a little and lasts 10-14 days. During treatment, this time can be shortened.
Other areas, here among the genitals, can also be affected by this virus. Once infected, you will carry the virus for the rest of your life, and will lie dormant until it is reactivated. It can also remain dormant forever, and you will therefore not discover you have been infected. Reactivation can occur through weakened immune system, sun, hormonal changes or trauma.
Herpes is transmitted by contact, and you can transmit the infection to others and to other places on your own body. It is very important that you do not touch your cold sore directly. In case of an outbreak, you can cover the wound with antiviral cream, take antiviral tablets, or cover the wound with a special patch for cold sores. As soon as you notice the first signs of an outbreak, treatment should begin.
Remember to inform your dentist if you have herpes so that both they and other patients are not at risk of being accidentally infected.
